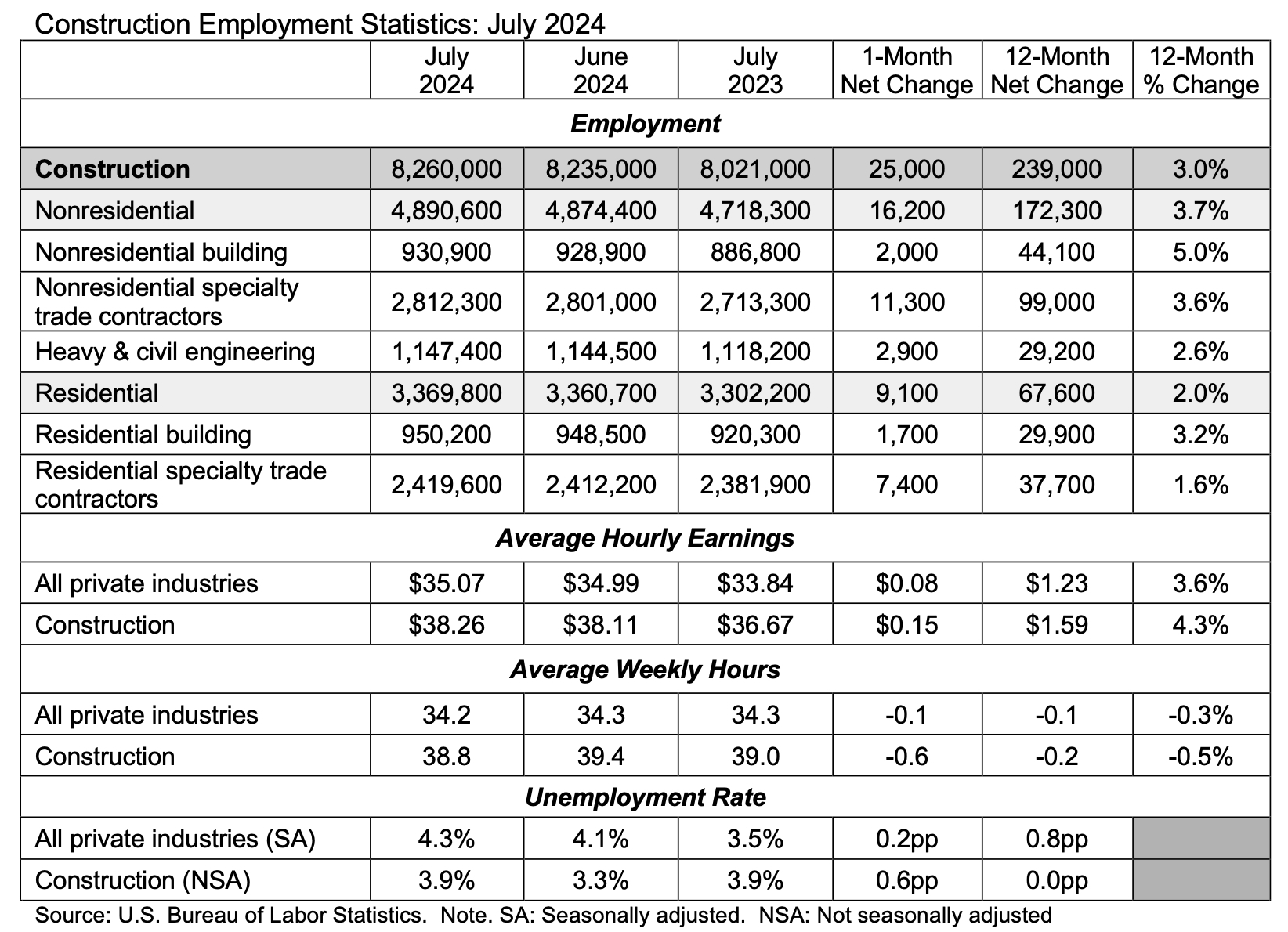
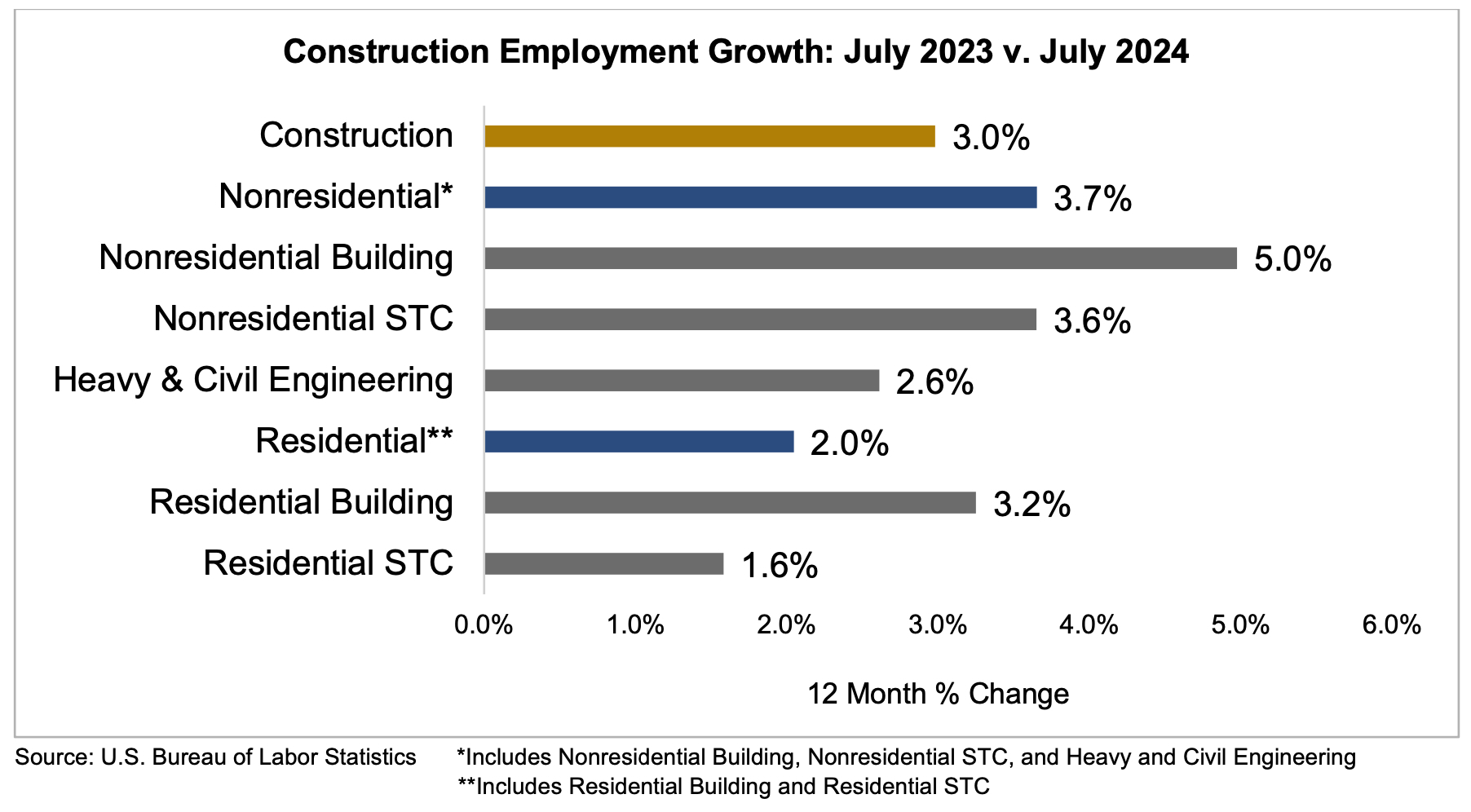
WASHINGTON (Aug. 2, 2024) — The construction industry added 25,000 jobs on net in July, according to an Associated Builders and Contractors (ABC) analysis of data released today by the U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics. On a year-over-year basis, industry employment has expanded by 239,000 jobs, an increase of 3.0%.
Nonresidential construction employment increased by 16,200 positions on net, with growth in all three subcategories. Nonresidential specialty trade contractors added the most jobs, increasing by 11,300 positions. Heavy and civil engineering and nonresidential building added 2,900 and 2,000 jobs, respectively.
The construction unemployment rate rose to 3.9% in July. Unemployment across all industries rose from 4.1% in June to 4.3% last month.
“It appears that America is headed into recession,” said ABC Chief Economist Anirban Basu. “While it is true that many economists have been suggesting this for more than two years, the recent slowing in economic activity feels different. Unemployment is climbing rapidly. Consumer spending growth has become more sluggish. U.S. equity markets are generating large losses, an indication that America is caught in a growth scare and that there is a growing consensus that the Federal Reserve has waited too long to begin reducing interest rates.
“Given that macroeconomic backdrop, it may seem peculiar that the U.S. construction industry managed to add 25,000 jobs in July,” said Basu. “How can one suggest that the U.S. economy is heading into recession when contractors are still eagerly hiring workers? In this regard, history is instructive. Nonresidential construction industry performance has tended to lag the performance of the overall economy by 12 to 18 months. According to ABC’s Construction Confidence Index, contractors collectively remain upbeat regarding their prospects for the next six months. But if the economy continues to weaken, and it appears poised to do precisely that, contractor confidence will begin to ebb. Indeed, the June construction spending data released on Aug. 1 indicate that many construction segments are already in slowdown mode.
“An exception to this is construction related to manufacturing,” said Basu. “The fastest segment of growth in construction spending has been in building construction, which encompasses massive investments in chip-making facilities and other industrial projects. Much of that is fueled in part by federal subsidies. But many construction segments do not benefit from federal subsidies, and those are the sectors that stand to experience the most erosion in performance as the economy softens and elevated borrowing costs linger.”